
While some law enforcement personnel have Crisis Intervention Training (CIT), the disability range covered by such training is limited to specific disability categories, as opposed to being comprehensive of a broader cross-disability standpoint grounded in a social model of accommodations over compliance. With limited options and the ways in which disability actions and behaviors present themselves, many calls get a police response – and sometimes an elevated police response. At this point, 911 operators must make the difficult decision of routing the call to the correct response. When community services are not provided at point of contact zero, a person with a disability, their family or the community may reach out to 911 for help. This point of contact is most commonly the entry point or deflection point into the criminal justice system. Peer representation is critical across all points of contact, but could have particular impact at point zero. These same entities should also ask whether people with disabilities and impacted community members are on their advisory boards and equally employed within their organizations. Where state and federal dollars come into play, state and federal disability civil rights law also apply.
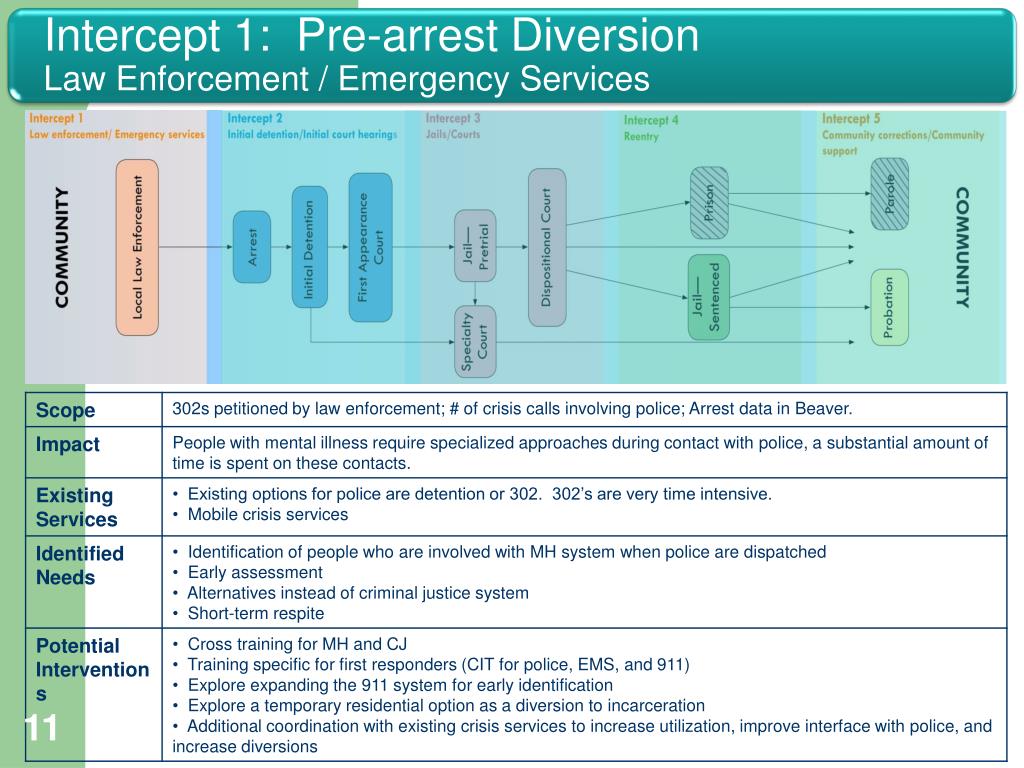
This includes budgeting for reasonable accommodations and including access features in new developments as well as rehab efforts of old facilities. Both government and funding organizations should hold providers accountable for designing accessibility accommodations as part of annual and long-term planning. Accessible community services can potentially contribute positively to a person’s avoiding other points of contact.Īccessibility at point of contact zero has to be intentional. Point of Contact Zero: Community ServicesĬommunity services that are accessible and affordable can provide people with disabilities what they need in the community and can be provided prior to a person engaging with the criminal justice system. Our interviews illuminated what it looks like when a person with a disability comes into contact at these different points. Point of Contact Five: Community Corrections Point of Contact Two: Initial Detention/Initial Court Hearings Point of Contact Zero: Community Services The SIM labels these points of contact (intercepts of the criminal justice system) zero though five, zero being prior to contact with the system and five being once a person goes through the justice system and is released on community supervision. This brief explanation can be used as an introductory overview of how the process might look when people with disabilities interact with the criminal justice system. This model is a way of breaking down the processes of the criminal justice system to view the processes in segments. The Sequential Intercept Model (SIM), originally developed more than 20 years ago, maps out different points of contact (intercepts) where community members interact with or are deflected from the criminal justice system.

Disability and the Sequential Intercept Model What is the SIM?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
